How Many Types of Transaction Security
There are two main types of transaction security: one is the use of encryption, and the other is the use of security keys. Using encryption in transactions will ensure that only the intended recipient has access to the information, and will prevent the information from being intercepted during transmission. Non-repudiability is another important transaction security feature, which protects against a recipient’s ability to deny receipt of a message or order.
In general, consumers are concerned about data privacy and security. Increasingly, they don’t want to do business with brands that have a bad transaction experience. A poor experience with a brand’s website can damage the brand image and make consumers less likely to come back. That’s why it’s critical for companies to implement a robust security solution. This type of solution is often called CIAM, or consumer identity and access management.
Most major credit card companies support these protocols, which allow merchants to verify card information without seeing it. This protects both the customer and the merchant from the risk of identity theft or hacking. In addition to encrypting the information, these protocols also prevent fraudulent transactions. These protocols are commonly used to protect online transactions.
Tokenization is another form of transaction security. This type of security involves replacing sensitive information with a token. This means that if a credit card is stolen, the fraudster won’t be able to use the information to make a purchase. Using the SET scheme ensures that the PI and OI can only be decrypted by the merchant and the acquiring bank.
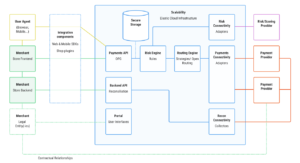
Types of Transaction Security
SET, or secure electronic transaction, is one of the first types of transaction security that was developed for internet-based transactions. This security protocol was developed by Microsoft and Netscape in order to protect credit card payments and ensure that the information was secure. The protocols involved symmetric and asymmetric cryptography, as well as a PKI to reliably distribute public keys.
A security exchange charge is demanded on each buy and offer of protections recorded on a perceived stock trade. The Government of India decides the STT rate. All securities exchange exchanges including value and value subsidiaries (choices and fates) are obligated for tax collection under the STT Act. When a buy or a deal exchange is fruitful, the STT is charged. Thus, the STT expands the expense of the exchange.
STT on actual conveyance of subordinates exchanges will be like STT on value share exchanges. This has been pronounced by the Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT) after a worry in regards to similar has been brought up in the Bombay High Court.
Securities Transaction Tax (STT) is a tax imposed on transactions between investors and sellers of securities on the Indian stock exchange. The rate is set by the Government of India. STT applies to equity transactions, stock options, and futures, which are both taxable in India. STT increases the cost of a transaction, but is not mandatory.